วิธีการวัดการคายประจุเองของแบตเตอรี่ลิเธียมไอออนส่วนใหญ่แบ่งออกเป็น 2 ประเภท: 1) วิธีการวัดแบบคงที่ ซึ่งได้อัตราการคายประจุเองโดยการยืนแบตเตอรี่เป็นเวลานาน; 2) วิธีการวัดแบบไดนามิกเพื่อให้ทราบถึงการระบุพารามิเตอร์ของแบตเตอรี่ในกระบวนการไดนามิก
วิธีการวัดแบบคงที่
ในปัจจุบัน วิธีการวัดการคายประจุเองของแบตเตอรี่ลิเธียมไอออนแบบกระแสหลักคือการทำให้แบตเตอรี่อยู่นิ่งเป็นเวลานานภายใต้สภาวะแวดล้อมบางอย่าง และวัดการเปลี่ยนแปลงของพารามิเตอร์ของแบตเตอรี่ก่อนและหลังไฟฟ้าสถิตเพื่อระบุระดับการคายประจุเองของลิเธียม- แบตเตอรี่ไอออน ตามพารามิเตอร์การวัดที่แตกต่างกัน การวัดแบบคงที่ส่วนใหญ่แบ่งออกเป็นสามประเภท: การวัดความจุ การวัดแรงดันวงจรเปิด และการวัดกระแส
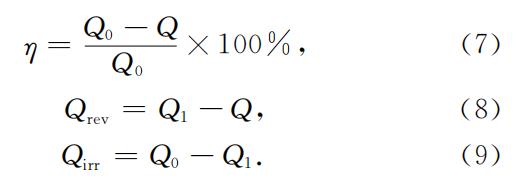
1. การวัดความจุ
ก่อนที่แบตเตอรี่จะใช้งานได้เป็นเวลานาน ให้ชาร์จและคายประจุแบตเตอรี่หนึ่งครั้ง และบันทึกความสามารถในการคายประจุ Q0 ก่อนที่จะหยุดทำงาน หลังจากยืน แบตเตอรี่จะถูกคายประจุในลักษณะเดียวกัน และความสามารถในการคายประจุ Q หลังจากยืนจะถูกบันทึก
According to equation (7), the self-discharge rate η of the battery can be calculated. Then the battery is charged and discharged in the same way, and the battery discharge capacity Q1 after the cycle is recorded. According to equations (8) and (9), the reversible self-discharge Qrev and irreversible self-discharge Qirr of the battery can be calculated respectively. A diagram of the method is shown in Figure 1.
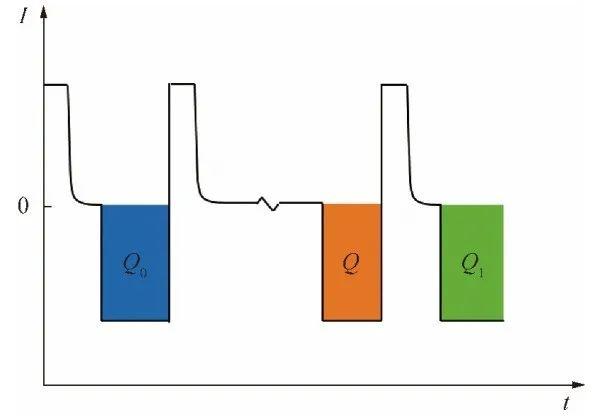
FIG. 1 Schematic diagram of capacity measurement method
In the battery testing manual issued by the international standardization bodies and relevant government departments and industry associations, the relevant provisions are made for the detection of battery self-discharge through capacity measurement: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) issued "Batteries and battery packs containing alkaline or other non-acidic electrolytes: Portable secondary lithium Batteries and accumulators "(IEC 61960) stipulates that the battery will be in the state of 50%SOC, stored at the ambient temperature of (20±5)℃ for 90 days, and the discharge of the battery after recharging should not be less than 85% of the rated capacity, the specific measurement process is shown in Figure 2a. The battery test manual for electric vehicles issued by the United States Automotive Research Council (USCAR) stipulates that the actual power level corresponding to the operating range of the battery should be measured before measurement. After the battery is discharged at a C/3 ratio of 50% of the available electricity, it is stored at an ambient temperature of 30 ° C for 30 days, and the discharge of the battery is measured after recharging. The "Performance Requirements and Test Methods of power batteries for Electric Vehicles" (GB/T 31486) issued by the Standardization Administration of China is similar to the IEC standard, which stipulates the measurement test process of charge retention and capacity recovery ability. Taking the room temperature test as an example, the battery is stored for 8d at room temperature, the charge retention rate is not less than 85% of the initial capacity, and the capacity recovery is not less than 90% of the initial capacity. The specific measurement process is shown in Figure 2b.

FIG. 2 Measurement procedure (a) specified in IEC 61960 and measurement procedure (b) specified in GB/T 31486
2. Open circuit voltage measurement
The self-discharge degree of lithium-ion battery is characterized by measuring the change of the open-circuit voltage during the battery resting process. The advantage of this method is that it is simpler and less time-consuming than measuring capacity. The disadvantage is that for lithium-ion batteries with a long voltage platform on the open volt-soc curve (such as LFP batteries), the battery voltage changes little in a large SOC range, and it is difficult to characterize the degree of self-discharge by measuring the open voltage, that is, the method has a certain range of application.
3. Current measurement
The lithium-ion battery is charged by micro-current to keep the battery voltage unchanged, and the charging current value when stable is self-discharge current [1-2]. This small current may not be stabilized for several months, and the stability time of different battery designs is different, and the generally recommended measurement time is at least one week [3].
This method has similar problems to the method of measuring open circuit voltage, that is, for lithium-ion batteries with long voltage platforms, the effectiveness of this method is challenged. In addition, because the self-discharge current of lithium-ion batteries is extremely small, generally C/50000 or lower, to apply and measure this tiny order of current, the requirements for experimental instruments are high.
The above conventional static current measurement method is improved to some extent. An electrochemical workstation is used to apply a constant voltage lower than the open current to the battery, and the current flowing through the circuit is measured at the same time. The current-time curve of the battery without self-discharge and the battery with self-discharge is shown in Figure 3a.
FIG. 3 Partial experimental results of Sazhin current measurement method
By actively applying a constant voltage, controlling the battery to reach the equilibrium state, and, measuring the current flowing through the circuit during this process, the measurement time can be shortened. In addition, the crossing point (CZCP) where the current is zero can also be used as a parameter to characterize the self-discharge rate. As shown in Figure 3b, the logarithm of tCZCP when the current Isc reaches zero is positively correlated with the logarithm of the self-discharge resistance Rself.
However, this method also has a serious disadvantage, that is, the accuracy of the experimental equipment is high. The electrochemical workstation used in the experiment has a voltage resolution of 100uV(14.5V range) and a current resolution of 1pA(200nA range).
Taken together, the above three methods are very time-consuming, with the experimental period ranging from one day to tens of days, and the reduction of the measurement time in the current measurement scenario requires high equipment costs.
Dynamic measurement method
Dynamic measurement method, that is, to realize the parameter identification of the battery in the dynamic process. To shorten the measurement time, save space resources and human resources. One method is to speed up the self-discharge rate by changing conditions such as the ambient temperature and SOC of the battery, so that the measurement parameters can change relatively large in a short period. Although this method saves the experiment time, it also speeds up the aging of the battery and increases the damage to the battery, which is only suitable for laboratory research and is not suitable for large-scale applications in actual production. Another method is to introduce self-discharge resistance based on the existing mature lithium-ion battery equivalent circuit model, and measure the self-discharge rate of lithium-ion batteries in the dynamic process through different parameter identification means.
Based on the automatic system identification theory, the lithium-ion battery is simplified into a first-order resistance-capacitance (R-C) equivalent circuit, and the same charge and discharge current is applied to the lithium-ion battery and the equivalent circuit, and the parameters of the equivalent circuit are adjusted according to the difference in output voltage until the difference between the two approaches zero, and the self-discharge resistance value of the lithium-ion battery is obtained. The total measurement time required for this method is about 12h. However, this method equates the battery to a passive circuit and does not consider the influence of the change of the battery's state of charge on the output voltage during the experiment.
Reduce the battery to an equivalent circuit as shown in Figure 4. Where: Rp, i is the electrochemical reaction resistance, Cp, i is the double electric layer capacitor, Rself is the self-discharge resistance, and C is the battery equivalent capacitance. Applying a short-time current pulse to the lithium-ion battery measures the voltage change during the subsequent resting process, and the self-discharge resistance value is further analyzed. This method only considers the reaction that plays a leading role in each stage of the static process and decouples the complex reactants, reducing the calculation and shortening the measurement time.
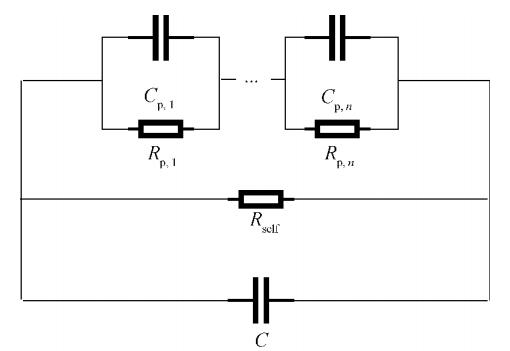
Figure 4 Lithium-ion battery equivalent circuit
Specifically, the recovery of overvoltage plays a leading role in the initial stage of static, and the self-discharge of the battery at the end of static plays a leading role. The time constant of self-discharge can be analyzed by the data at the end of the static period, and then the voltage drop caused by self-discharge in the recovery period of overvoltage can be compensated, and the equivalent capacitance of the battery can be solved, and the self-discharge resistance value can be obtained. This method can obtain the self-discharge resistance of lithium-ion batteries within 10 ~ 48h, saving a lot of time compared with the traditional method, but it still needs to consume a lot of static time to observe the stage where self-discharge plays a dominant role.
ผลกระทบของการลัดวงจรในแบตเตอรี่แบ่งออกเป็นสองประเภท: ผลกระทบจากพารามิเตอร์และผลกระทบจากการบริโภค ในหมู่พวกเขา: ผลกระทบของพารามิเตอร์หมายความว่าเนื่องจากการมีอยู่ของความต้านทานไฟฟ้าลัดวงจร แรงดันไฟฟ้าวงจรเปิดที่วัดได้และความต้านทานภายในมีค่าเบี่ยงเบนจากค่าจริง ผลการบริโภคหมายความว่าเนื่องจากการมีอยู่ของความต้านทานไฟฟ้าลัดวงจร พลังงานที่เก็บไว้ภายในแบตเตอรี่จะถูกใช้อย่างต่อเนื่อง และ SOC ของแบตเตอรี่จะลดลงอย่างต่อเนื่อง ซึ่งจะนำไปสู่การเบี่ยงเบนของค่าที่แท้จริงของแรงดันวงจรเปิดของแบตเตอรี่และ ความต้านทานภายในจากค่าปกติ

ในแบบจำลองความแตกต่างของแบตเตอรี่ที่แสดงในสูตร (10) และ (11) Ei คือแรงดันวงจรเปิดของแบตเตอรี่ Ri คือความต้านทานภายในของแบตเตอรี่ และ Ui และฉันคือแรงดันและกระแสของแบตเตอรี่ที่วัดได้ตามลำดับ ค่าของ ΔEi และ ΔRi ได้มาจากวิธีกำลังสองน้อยที่สุดแบบเรียกซ้ำ และค่าพารามิเตอร์ที่ผิดปกติที่เกินค่าเกณฑ์จะถูกระบุด้วยวิธีทางสถิติเพื่อระบุว่าแบตเตอรี่มีการลัดวงจรภายในหรือไม่ เมื่อค่าความต้านทานไฟฟ้าลัดวงจรเท่ากับ 100Ω วิธีการนี้สามารถระบุการลัดวงจรภายในได้เร็วที่สุดภายในเวลา 4 ชั่วโมง 43 นาที
วิธีการวัดไดนามิกสามวิธีข้างต้นทำให้แบตเตอรี่ลิเธียมไอออนง่ายขึ้นโดยการใช้วงจรสมมูลและวิธีการอื่นๆ และนำวิธีการทดลองที่เป็นนวัตกรรมใหม่มาใช้ในการวิเคราะห์ค่าความต้านทานการคายประจุเอง ซึ่งมีความคืบหน้าอย่างมากในการย่นระยะเวลาการวัด
สรุปผล
มีการทบทวนวิธีการวัดอัตราการคายประจุตัวเองของแบตเตอรี่ลิเธียมไอออนโดยการวัดแบบสถิตและการวัดแบบไดนามิก ข้อสรุปหลักมีดังนี้:
1, ปฏิกิริยาด้านข้างที่เกิดขึ้นที่ขั้วลบ/อิเล็กโทรไลต์และขั้วบวก/อิเล็กโทรไลต์อินเทอร์เฟซเป็นแหล่งหลักของการปลดปล่อยตัวเองของแบตเตอรี่ลิเธียมไอออน, สามารถแก้ไขได้โดยพื้นผิวของขั้วบวก, การเติมสารเติมแต่งในขั้วลบ อิเล็กโทรไลต์ และวิธีการอื่น ๆ เพื่อยับยั้งการเกิดการปลดปล่อยตัวเอง
2 ในกระบวนการจัดเก็บแบตเตอรี่ ควรพยายามหลีกเลี่ยงการอยู่ในสถานะ SOC สูงหรือต่ำเกินไป และอุณหภูมิและความชื้นโดยรอบควรอยู่ในช่วงที่ค่อนข้างต่ำ
3. วิธีการวัดการคายประจุเองกระแสหลักในปัจจุบันคือการวัดแบบสถิตตามการทดลองทางสถิตระยะยาว ปัญหาที่ใหญ่ที่สุดของวิธีนี้คือเวลาในการตรวจวัดนานเกินไป ทำให้สิ้นเปลืองพื้นที่และทรัพยากรบุคคลอย่างมาก มีการเสนอวิธีการวัดไดนามิกบางอย่างสำหรับการระบุพารามิเตอร์รวมกับแบบจำลองวงจรสมมูล และความคืบหน้าบางอย่างทำให้เวลาในการวัดสั้นลง ด้วยการออกแบบเชิงทดลองที่เป็นนวัตกรรมใหม่ การแยกการระบุการปลดปล่อยตัวเองในกระบวนการไดนามิกคือเส้นทางสำคัญและทิศทางการพัฒนาสำหรับการวัดการปลดปล่อยตัวเองอย่างรวดเร็วในอนาคต
หมวดหมู่
ล่าสุด โพสต์
สแกนไปที่ WeChat:everexceed
